近期,由爱都科技领军人物“何岸先生”联合华南理工大学各学院及产业技术研究所、暨南大学第一附属医院等机构,于国际知名学术期刊《Biomedical Signal Processing and Control》上联合发布了最新学术论文《A new approach for daily life Blood-Pressure estimation using smart watch》(一种使用智能手表在日常生活中进行血压预测的新方法)。此篇论文的内容引用了爱都科技智能穿戴技术研究院先进的技术及研究成果,论文在国际核心期刊上的采纳与发布,表明了爱都的研究成果得到了学术界的认可与赞誉。
秉持着“技术服务于产品,产品服务于客户”的理念,爱都科技在智能穿戴领域不断精进技术研究,利用先进的技术打造产品,更好地服务于全球各地的消费者。

Highlights
• Wearable ECG and PPG dataset was established by using a highly integrated smart watch.
• The features of PPG and ECG were fused to extract blood-pressure relevance information.
• The 5-s physiological data segments were selected by using the outlier detection algorithm.
• A calib-free mode and a calib-based mode were presented for blood-pressure monitoring.
• 使用高度集成的智能手表建立了可穿戴心电图和PPG数据集。
• 融合PPG和ECG的特征,提取血压相关信息。
• 通过使用异常值检测算法选择5-s生理数据段。
• 提出了用于血压监测的无校准模式和基于校准的模式。
Abstract
Hypertension has become a major factor affecting people’s health. Timely monitoring and prevention of hypertension are of great significance. Most blood-pressure monitoring devices have redundant accessories and complex operations, which are not suitable for daily life applications. To solve these problems, we designed an application-level smart watch that can calculate the PAT feature using simultaneously collected ECG and PPG signals. By fusing the time–frequency-domain features of PPG and the correlation matrix between pulses, the information related to blood pressure in physiological signals was comprehensively extracted. Most of unstable signal segments can be eliminated and the impact of signal disturbances on overall accuracy will be reduced. This paper proposed two blood-pressure estimation modes: a two-step calib-free mode and a personal calibration mode based on transfer learning. The results on our self-established dataset (36 normotensive subjects and 40 hypertensive subjects) indicated that the two-step calib-free mode could estimate blood pressure with accuracy of 0.23 ± 6.1 mmHg and 0.63 ± 9.35 mmHg for DBP and SBP respectively, which was better than previous calib-free methods. Through the personal calibration mode, the estimation accuracy reached 0.02 ± 5.94 mmHg for DBP and 0.3 ± 7.69 mmHg for SBP, which complied with the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation standard.
高血压已成为影响人们健康的主要因素,及时监测和预防对控制高血压具有重要意义。大多数血压监测设备配件冗余,操作复杂,不适合日常生活应用。为了解决这些问题,我们设计了一款应用级智能手表,可以通过同时采集的 ECG 和 PPG 信号来计算 PAT 特征。通过融合PPG的时频域特征和脉冲间的相关矩阵,综合提取生理信号中与血压相关的信息。可以消除大部分不稳定的信号段,减少信号扰动对整体精度的影响。本文提出了两种血压估计模式:两步无校准模式和基于迁移学习的个人校准模式。我们自建的数据集(36 名血压正常受试者和 40 名高血压受试者)的结果表明,两步无校准模式可以估计血压,DBP 和 SBP 的准确度分别为 0.23 ± 6.1 mmHg 和 0.63 ± 9.35 mmHg,这比以前的无校准方法更好。通过个人校准模式,DBP的估计精度达到0.02±5.94 mmHg,SBP的估计精度达到0.3±7.69 mmHg,符合医疗器械促进会标准。

《Biomedical Signal Processing and Control》
《生物医学信号处理与控制》旨在为临床医学和生物科学中信号和图像的测量和分析研究信息的交流提供一个跨学科的国际论坛。 重点放在对在临床诊断、患者监测和管理中使用方法和设备进行实用的、以应用为导向的研究方面的贡献。生物医学信号处理和控制反映了这些方法在工程和临床科学的界面上被使用和开发的主要领域。该期刊的范围被定义为包括相关的评论论文、技术说明、简短的通信和信件。 教程论文和特刊也将出版。
该期刊是欧洲医学和生物工程与科学联盟(EAMBES)的官方期刊。
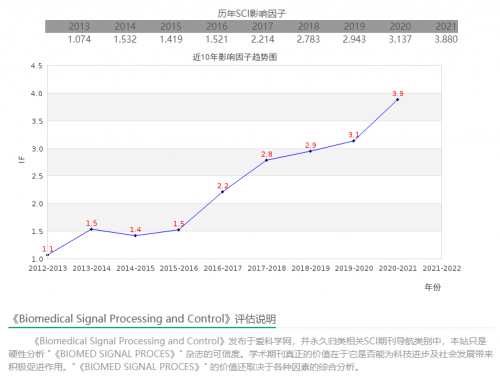
该期刊是SCI 期刊, IF(Impact Factor)是3.880。论文影响因子(Impact Factor,IF)是 Thomson Reuters出品的期刊引证报告(Journal Citation Reports )中的一项数据。 即某期刊前两年发表的论文在该报告年份中被引用总次数除以该期刊在这两年内发表的论文总数。IF影响因子现已成为国际上通用的期刊评价指标,它不仅是一种测度期刊有用性和显示度的指标,而且也是测度期刊的学术水平,乃至论文质量的重要指标。
免责声明:市场有风险,选择需谨慎!此文仅供参考,不作买卖依据。

